05
Oct
2021
Zoom Image in SwiftUI
Reading time: 4 min
This recipe shows how to zoom an image in SwiftUI using the pinch/magnify gesture. The image is zoomed in or out at the midpoint between the fingers, supports dragging and double tap to zoom in or reset.
The end result looks like this:
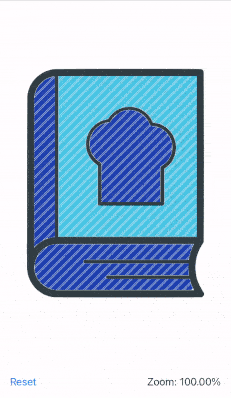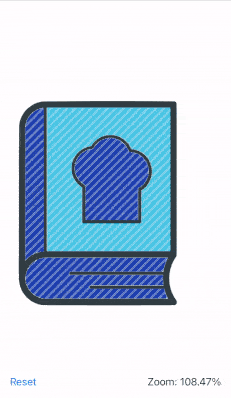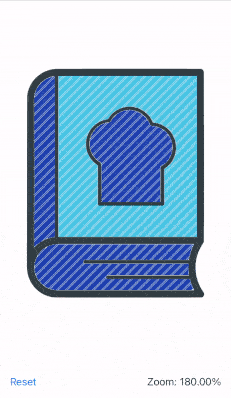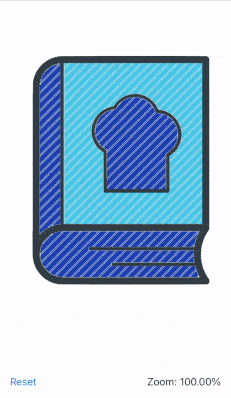
The recipe goes as follows:
- Use a custom
UIVIewwithUIPinchGestureRecognizer. This allows you to track the anchor point, which is the point midway between the fingers. The fact that we're zooming in based on the anchor point will result in an offset of the zoomed view. - Wrap that custom view via
UIViewRepresentable, and allow it to publish its current scale factor, anchor point and offset. - Put the wrapped
Viewas an overlay to the content ofViewModifierto capture the gesture, and use its bindings to modify thescaleEffectandoffset. - Optionally, add a
TapGestureto support double taps for quickly zooming in or resetting.
// Constrains a value between the limits
func clamp(_ value: CGFloat, _ minValue: CGFloat, _ maxValue: CGFloat) -> CGFloat {
min(maxValue, max(minValue, value))
}
// UIView that relies on UIPinchGestureRecognizer to detect scale, anchor point and offset
class ZoomableView: UIView {
let minScale: CGFloat
let maxScale: CGFloat
let scaleChange: (CGFloat) -> Void
let anchorChange: (UnitPoint) -> Void
let offsetChange: (CGSize) -> Void
private var scale: CGFloat = 1 {
didSet {
scaleChange(scale)
}
}
private var anchor: UnitPoint = .center {
didSet {
anchorChange(anchor)
}
}
private var offset: CGSize = .zero {
didSet {
offsetChange(offset)
}
}
private var isPinching: Bool = false
private var startLocation: CGPoint = .zero
private var location: CGPoint = .zero
private var numberOfTouches: Int = 0
// track the previous scale to allow for incremental zooms in/out
// with multiple sequential pinches
private var prevScale: CGFloat = 0
init(minScale: CGFloat,
maxScale: CGFloat,
scaleChange: @escaping (CGFloat) -> Void,
anchorChange: @escaping (UnitPoint) -> Void,
offsetChange: @escaping (CGSize) -> Void) {
self.minScale = minScale
self.maxScale = maxScale
self.scaleChange = scaleChange
self.anchorChange = anchorChange
self.offsetChange = offsetChange
super.init(frame: .zero)
let pinchGesture = UIPinchGestureRecognizer(target: self, action: #selector(pinch(gesture:)))
pinchGesture.cancelsTouchesInView = false
addGestureRecognizer(pinchGesture)
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
fatalError()
}
@objc private func pinch(gesture: UIPinchGestureRecognizer) {
switch gesture.state {
case .began:
isPinching = true
startLocation = gesture.location(in: self)
anchor = UnitPoint(x: startLocation.x / bounds.width, y: startLocation.y / bounds.height)
numberOfTouches = gesture.numberOfTouches
prevScale = scale
case .changed:
if gesture.numberOfTouches != numberOfTouches {
let newLocation = gesture.location(in: self)
let jumpDifference = CGSize(width: newLocation.x - location.x, height: newLocation.y - location.y)
startLocation = CGPoint(x: startLocation.x + jumpDifference.width, y: startLocation.y + jumpDifference.height)
numberOfTouches = gesture.numberOfTouches
}
scale = clamp(prevScale * gesture.scale, minScale, maxScale)
location = gesture.location(in: self)
offset = CGSize(width: location.x - startLocation.x, height: location.y - startLocation.y)
case .possible, .cancelled, .failed:
isPinching = false
scale = 1.0
anchor = .center
offset = .zero
case .ended:
isPinching = false
@unknown default:
break
}
}
}
// Wraps ZoomableView and exposes it to SwiftUI
struct ZoomableOverlay: UIViewRepresentable {
@Binding var scale: CGFloat
@Binding var anchor: UnitPoint
@Binding var offset: CGSize
let minScale: CGFloat
let maxScale: CGFloat
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ZoomableView {
let uiView = ZoomableView(minScale: minScale,
maxScale: maxScale,
scaleChange: { scale = $0 },
anchorChange: { anchor = $0 },
offsetChange: { offset = $0 })
return uiView
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ZoomableView, context: Context) { }
}
// Applies ZoomableOverlay to intercept gestures and apply scale,
// anchor point and offset
struct Zoomable: ViewModifier {
@Binding var scale: CGFloat
@State private var anchor: UnitPoint = .center
@State private var offset: CGSize = .zero
let minScale: CGFloat
let maxScale: CGFloat
init(scale: Binding<CGFloat>,
minScale: CGFloat,
maxScale: CGFloat) {
_scale = scale
self.minScale = minScale
self.maxScale = maxScale
}
func body(content: Content) -> some View {
content
.scaleEffect(scale, anchor: anchor)
.offset(offset)
.animation(.spring()) // looks more natural
.overlay(ZoomableOverlay(scale: $scale,
anchor: $anchor,
offset: $offset,
minScale: minScale,
maxScale: maxScale))
.gesture(TapGesture(count: 2).onEnded {
if scale != 1 { // reset the scale
scale = clamp(1, minScale, maxScale)
anchor = .center
offset = .zero
} else { // quick zoom
scale = clamp(2, minScale, maxScale)
}
})
}
}
extension View {
func zoomable(scale: Binding<CGFloat>,
minScale: CGFloat = 0.5,
maxScale: CGFloat = 3) -> some View {
modifier(Zoomable(scale: scale, minScale: minScale, maxScale: maxScale))
}
}Finally, here's some sample usage:
struct ZoomableTest: View {
@State private var scale: CGFloat = 1
var body: some View {
VStack {
Spacer()
Image("icon")
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.zoomable(scale: $scale)
Spacer()
HStack {
Button("Reset") {
scale = 1
}
Spacer()
Text("Zoom: \(String(format: "%.02f", scale * 100) )%")
}
.padding()
}
}
}