Reading time: 1 min
This recipe shows how to set visibility of a SwiftUI view. You can show it, hide it, or remove it from the view hierarchy entirely.
The end result looks like this:
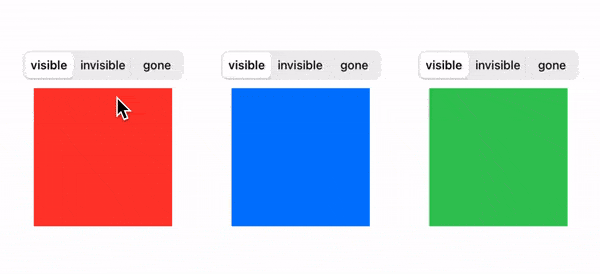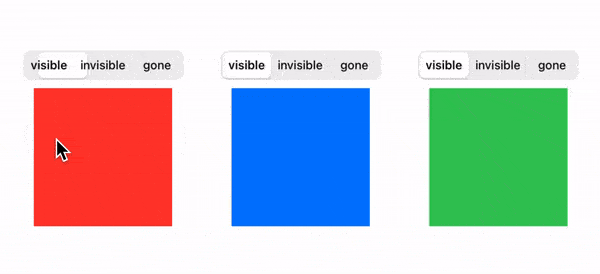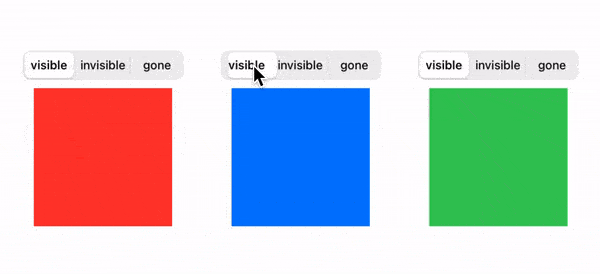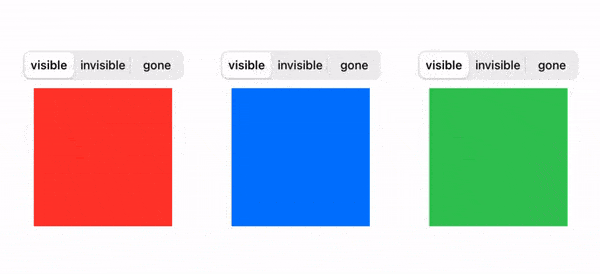
We'll adopt a good practice from Android and model the view visibility like this:
enum ViewVisibility: CaseIterable {
case visible, // view is fully visible
invisible, // view is hidden but takes up space
gone // view is fully removed from the view hierarchy
}Then, we can use it with this extension:
extension View {
@ViewBuilder func visibility(_ visibility: ViewVisibility) -> some View {
if visibility != .gone {
if visibility == .visible {
self
} else {
hidden()
}
}
}
}All done! You can now change your view's visibility with ease:
Text("Some text")
.visibility(.invisible)
Text("Some other text")
.visibility(.gone)To wrap things up, here's the code of the sample above, which shows how to change the visibility based on state change:
struct VisibilityTestView: View {
@State private var redVisibility: ViewVisibility = .visible
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 10) {
Picker("Picker", selection: $redVisibility) {
ForEach(ViewVisibility.allCases, id: \.self) { visibility in
Text(String(describing: visibility))
.id(visibility)
}
}
.pickerStyle(SegmentedPickerStyle())
Rectangle()
.fill(Color.red)
.frame(width: 150, height: 150)
.visibility(redVisibility)
}
}
}